Stone diseases Urinary stone disease / Kidney stone disease
Did you know that every tenth person on the planet will have at least one kidney stone during their lifetime? Recent studies have shown that the number of people suffering from urolithiasis is growing every year around the world. Over the past 30 years, their number has increased every 3 years by almost 5%. Such a trend is observed both among men and among different women races The risk of kidney stone formation in men is about 18%, and in women - 10%. IN in men, the first episode is most likely already at the age of 30. The peak incidence falls on forty years old.
Kidney stones occur even in children as young as 5 years old. In fact, this problem is very common among children of such countries as, for example, the USA. This can be explained mostly wrong diet. Studies have shown that the majority of children diagnosed with urolithiasis, eat mainly fast food, canned foods and carbonated sweet drinks.
At an early stage, urolithiasis often has no symptoms and can remain unnoticed until it reaches the level of serious manifestations. But a simple urine test will help determine if you have kidney disease. It should be noted that early detection and treatment can slow down or prevent the progression of urolithiasis.
'Symptoms of urolithiasis
Kidney stones (calculi) have different sizes and shapes depending on their composition, causes and conditions formation. As a rule, the larger the stone, the more noticeable the symptoms.
Symptoms of kidney stones:
- frequent urges to urinate, but urine comes out in small portions
- difficult urination
- severe sharp pain from the affected kidney in the lower back
- aching / pulling pain in the abdomen or groin, pain that does not go away
- blood in urine
- nausea or vomiting
- fever and chills
- urine that smells bad or looks cloudy
Consequences of having a kidney stone
In a number of cases, the presence of kidney stones can lead to a condition known as "renal." colic". It is believed that the pain of renal colic is one of the strongest that one can feel a person, and in terms of intensity of influence it surpasses even childbirth.
The kidney starts to hurt when the stone causes irritation or blockage. In some cases pain is growing rapidly. Often small kidney stones are washed out with urine without causing any harm harm or intense pain. Painkillers may be the only method of treatment small stones For stones that cause long-term symptoms or other complications, another treatment is needed. In difficult cases, surgical intervention may be required.

Renal colic with’occurs when a stone causes blockage of a kidney segment or ureter, which leads to overstretching of the kidney capsule, where pain receptors are located. Urate stones up to 4 mm can come out on their own when using therapy with citrate mixtures and antispasmodics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, painkillers, although there is a risk the occurrence of a complication, such as, for example, acute obstructive secondary pyelonephritis. Therefore, the faster the blocked kidney will be drained, that is, the faster the outflow of urine will be restored, the better.
Consequences of having a kidney stone
- First, kidney stones increase the risk of developing chronic kidney disease: pyelonephritis, kidney cysts, cystitis, increased pain syndrome.
- Second, if you develop at least one kidney stone, you have a 50% risk the development of another during the next 5-7 years.
Types of kidney stones
Why do you need to study the content of the stone?
If you have at least one of the above symptoms, you should contact us as soon as possible to the doctor. If you have a stone on your own, it is advisable to bring it to the doctor for an accurate diagnosis definition of its type. Studying the stone will help to understand the reasons for the formation, to determine ways to remove them (if there are several stones) and reduce the risk of new ones.
The determination of stone density during computer tomography is of great importance, which is measured in Hounsfield units (HU). It is also recommended to pass a daily urine analysis on salt and salt transport analysis, determine the level of blood parathyroid hormone, ionized calcium blood, etc.
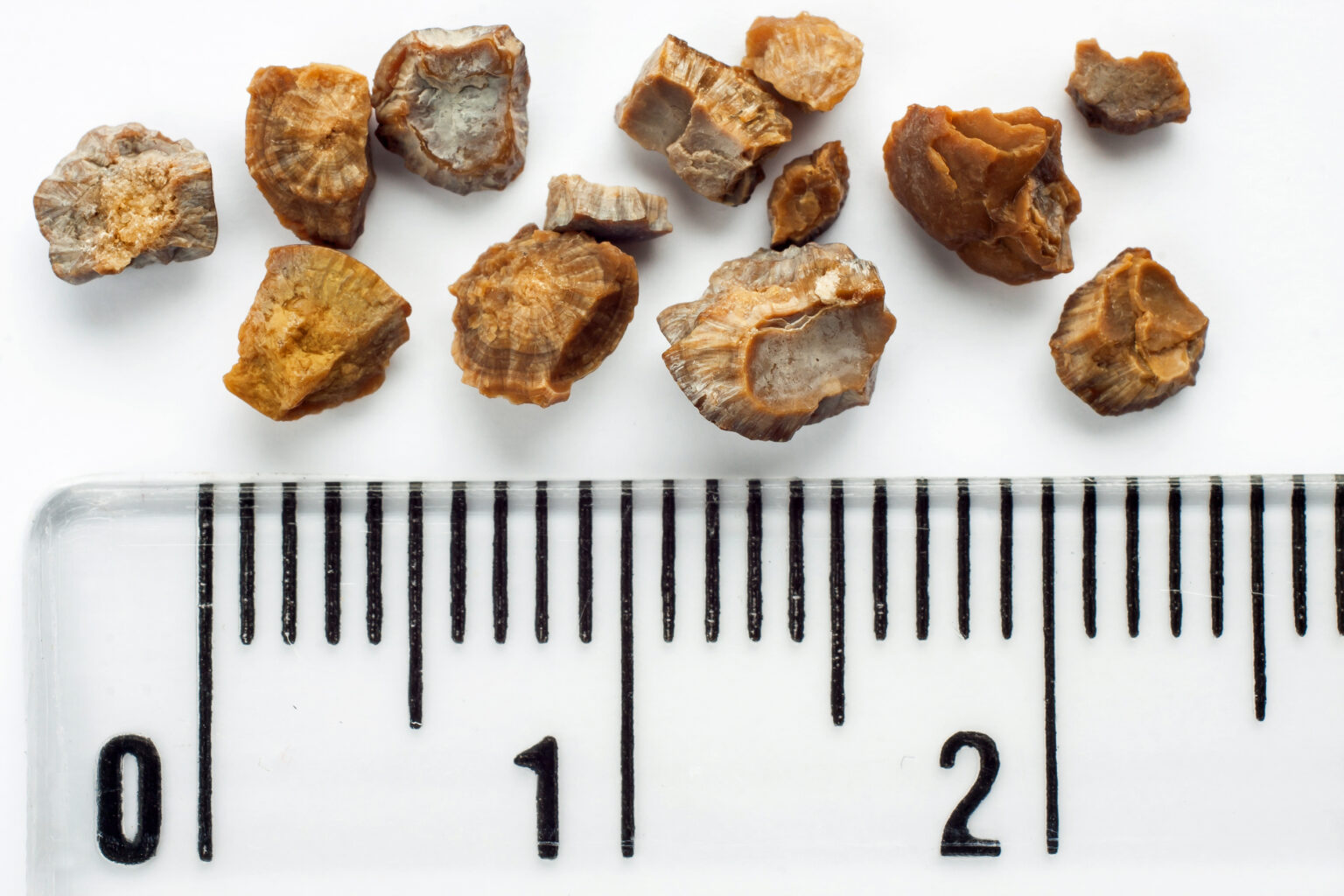

The most common type of kidney stone contains calcium. It is an important part of healthy food. The kidney usually removes excess calcium from the body. But sometimes calcium accumulates too much, and in combination with other substances that are formed in as a result of metabolism, such as oxalate, a stone is formed. The most common combination is called calcium oxalate.
Less common types of stones are those that:
- contain magnesium and ammonia, the so-called struvite concretions, they occur during infection urinary tract;
- formed from monosodium sodium urate crystals (urate stones), which are also called stones uric acid,
- the rarest type of stone is cystine, which is formed, as a rule, as a result family heredity or genetic predisposition.
Types of kidney stones
A stone in the kidneys (kidney calculus) is a dense formation that consists of chemicals substances in the urine. If there is too little fluid in the kidneys and bladder too much waste is concentrated, it begins to crystallize. Chemical stone-forming substances are calcium, urate, oxalate, cystine, xanthine, and phosphate. IN For most people, drinking enough fluids helps flush these chemicals out of the body urine, which prevents stone formation.But in people prone to urolithiasis, crystals attract other elements, unite and increase in size. A stone can remain in the kidney or pass through the urinary tract into the ureter. Sometimes tiny stones leave the body with urine without causing much pain. But stones that are stuck and not move, as a rule, they cause the accumulation of urine in the kidneys, ureters, and bladder or urethra, causing pain and inflammation of the urinary system.

Kidney stones are classified by the cause of their occurrence into non-infectious, infectious, genetic and medicinal.
Non-infectious:
1. Calcium oxalates is the most common type of kidney stone that forms from salts of oxalic acid, when calcium from’combined with oxalate in urine. If the size oxalate kidney stones exceed one and a half centimeters, surgical removal is necessary.
2. Урати is another common type of kidney stone. They are formed from salts uric acid for a low indicator of the balance of alkalis and acids. Food consumption, which have a high concentration of the natural chemical compound purines, increases the formation of sodium urate in the body, which under certain conditions can form kidney stones. Most often urate stones are removed with the help of drug treatment. Before immediate removal succeed in 5% of cases.
3. Calcium phosphates there are two types, of which bruchitis is non-infectious origin. Stones, which include calcium phosphates, tend to increase rapidly. Since the stones of that group consist mainly of alkalis, they are easily crushed and dissolving In most cases, it is quite correct to remove phosphate stones drug therapy and adherence to diet.
Infectious calculi these are stones, the cause of which are infectious and inflammatory processes of the urinary system. Concretions belong to this group flow (magnesium and ammonium phosphate), carbonate-apatite, ammonium urate. Almost all stones of this group require immediate removal.
To genetically determined concretions belong cystine, xatin, dihydroxyadedine. Stones of this group are most often removed surgically.
Medical concretions are formed in the kidneys as a result of improper taking medicines. There are also medical preparations that provoke changes in the composition urine, thereby contributing to the formation of stones. Treatment of medicinal stones in the kidneys they start with stopping taking the drugs that caused their formation. For example: patients, who take sulfonamide drugs (antipyretic drugs), should consume a large the amount of alkaline liquid (up to 3 liters per day).
Basic recommendations for the prevention of urolithiasis
A healthy lifestyle as a way to prevent urolithiasis
One of the easiest ways to prevent CKD is the correct drinking regime! The general rule is 40 ml of liquid per 1 kg of body weight per day or focusing on diuresis 2 liters of urine per day!
Drinking a sufficient amount of liquid helps to maintain the correct concentration of various substances in the urine. The color of urine is an indicator of such concentration. The darker the urine, the better it is more concentrated In order for the body to clean itself well, your urine should be light yellow color.
Щонайменше половина рідини, яку ви п’єте, має бути вода. Більшості людей необхідно пити в середньому 2-3 літри води на день. У спекотну погоду, і якщо ви займаєтеся спортом, вам слід пити більше. Бажано також зменшити вживання газованих напоїв, особливо солодких, а також кави і міцного чаю.

Систематичне підвищене потовиділення (через спекотну погоду, важкі фізичні навантаження, регулярні відвідування сауни або лазні) також може сприяти формуванню ниркових каменів. Чим більше ви потієте, тим менше виробляється сечі, що дозволяє мінералам, які утворюють камені, осідати і відкладатися в нирках і сечових шляхах через зниження швидкості потоку і об’єму сечі.
RECOMMENDATION: With increased sweating, increase the amount of liquid that you drink, preferably water. Try to avoid sugary drinks, especially carbonated and grape juice
Choosing the right diet that corresponds to your indicator is of great importance urine pH to maintain a healthy acid-base balance in the body.
For example, a diet with a lot of fruits and vegetables makes urine less acidic. And animal protein, on the contrary, increases the level of acidity of urine, which can increase the risk of developing such kidney stones, such as urate stones.

It is necessary to resort to the so-called with caution and only after consulting a professional nutritionist protein diets for weight loss (especially with a high content of animal proteins).
It is necessary to minimize the consumption of products with a high content of salt, sugar and carcinogens
Chips, fast food, canned food, fast food, sports and soda it is desirable to consume drinks as rarely as possible, and it is better to completely exclude them from the diet, because they consist of concentrates, essences and acids.
Calcium is important for human health! But how to avoid the formation of renal calcium stones?
A leading role in this process is played by a correct understanding of the importance of calcium for humans body and the correct use of calcium-containing products, medicinal and dietary products supplements with this trace element.
Do not be afraid to use products containing calcium. In fact, they are mostly dairy products help prevent the formation of kidney stones, as it binds calcium with oxalate (the most common type of kidney stone) before it reaches the kidneys. Simply conversely, people who consume little dietary calcium have an increased risk of kidney stones stones Levels of oxalate, a byproduct of metabolism, rise if the body does not enough liquid, and if there is too much salt. It is connected under these conditions with calcium, forming kidney stones.
The main methods of treatment of urolithiasis
Treatment methods for urolithiasis depend on several factors, such as the number, size, shape and type kidney stones.
- Small stones are usually removed naturally, increasing in number liquid that is drunk. Sometimes, in such cases, the doctor can only prescribe the patient painkillers and antispasmodics.
- Depending on the type of kidney stones, the patient may be prescribed medication that lowers the level acidity of urine and dissolve these stones to the size when they can come out on their own along with urine. As a rule, this method is used to dissolve urate stones using citrate mixtures.
- Medicinal litholysis with citrate mixtures.
- Combining with water in the body, citrate mixtures have an alkalizing effect and create increased concentration of sodium and potassium ions in urine. It normalizes the reaction of urine and brings it closer to neutral indicators (pH 6.6-6.8). Under such conditions, it increases significantly the solubility of uric acid salts and increased excretion of potassium, and this prevents formation of urate concretions.
- Keeping urine acidity in the range of 7.0-7.2 allows you to dissolve already existing ones urate stones in the kidneys.
- For large stones of other types, a surgical method can also be used or non-invasive crushing method. Shock wave lithotripsy this a non-invasive procedure that uses directional ultrasound waves to break up large kidney stones into small fragments, which are then more easily excreted naturally by the flow of urine.
- If the kidney stone is too large, or if it blocks the flow of urine, are there signs infection or inflammation, it is removed surgically, usually through one of the procedures, specified below.
Urethroscopy is a method of visual diagnosis of the urethra (urethra), which is carried out with the help of a special device (optical endoscope) - a ureteroscope or urethrocystoscope. This device is also used to remove stones through the ureter.
Contact laser lithotripsy this is a high-tech method of destruction any type of kidney, ureter and bladder stones. During the procedure, the doctor through the urinary tract leads to the stone with a mini video camera and a special laser a lithotripter probe that destroys stones into small fragments and sand. It is used for contact crushing of stones in the middle and lower thirds of the ureter.
For very large or complex stones, especially coral-like stones, doctors use percutaneous (percutaneous) nephrolithotomy / nephrolithotripsy.
Percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL) – surgical operation to remove stones from kidneys through a minimal puncture hole in the lumbar region (skin incision - usually up to 12 mm).
Percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL) considered one of the most effective and safe methods of removing kidney stones, the essence of which is percutaneous introduction into the kidney system of endoscopic instruments for crushing and removing stones. Fragmentation stones are carried out by the contact method, affecting them with a shock wave. Removal smaller fragments are performed using endoscopic instruments. This procedure performed in patients who are contraindicated for another non-invasive method of stone removal - ESWT (remote shock wave lithotripsy).